Amblygonite may look like just another crystal at first glance, but hidden within its structure is a story that stretches back over two hundred years, from its discovery in 1817 to its rare transformation into faceted gems. In this guide, let’s uncover its history, scientific importance, and why collectors continue to seek this uncommon mineral.
Amblygonite meaning
Connection to inner balance: Amblygonite has long been recognized in metaphysical traditions as a stone associated with internal balance, and people have often described it as holding qualities that may bring calm when life feels full of activity. Its presence in collections of crystals and stones is sometimes linked to practices where individuals want a sense of quiet within, and this mineral has been considered a way to create a bridge between emotional awareness and thoughtful clarity. The structure of this phosphate mineral, which often appears in pale tones, carries an association with reflective practices that allow attention to shift inward in a steady manner.
Spiritual growth: Within the world of healing crystals, amblygonite is seen as a mineral that may encourage reflection on spiritual ideas, particularly when a person seeks deeper meaning or connection beyond everyday experiences. It has been described in some writings as offering qualities that could expand awareness during meditation, especially when people hold or focus on tumbled stone forms. Some view this gemstone as a companion for journeys into higher states of awareness, where the vibration of amethyst crystal or white quartz might also be present, creating a combined setting that supports intuitive exploration.
Emotional healing: In metaphysical use, amblygonite has been connected to processes involving emotional healing, as it is often thought to bring an energy that helps release past burdens. Many consider it alongside crystals like purple amethyst or green prasiolite when working toward emotional balance, since the mix of different gemstones may strengthen a sense of stability. Its reputation within crystal circles includes associations with calm energy, supporting thoughtful focus on personal growth. This crystal is sometimes seen as part of groupings that also include tourmaline or moldavite, where the combination is said to foster creative and compassionate perspectives.
Energy flow: Amblygonite is frequently mentioned in connection with the chakras, especially those regarded as higher centers such as the crown chakra, where many believe spiritual awareness becomes stronger. By placing amblygonite near these areas, practitioners often describe a flow of energy that blends with the balancing vibration of other stones, including chevron amethyst or phenacite. Its reputation in metaphysical circles often centers on creating alignment between thoughts and intuitive awareness, which may feel valuable in practices like meditation or spiritual study. Over time, this gemstone has gained a place among crystals chosen for work involving divine light, emotional balance, and connection with higher realms.
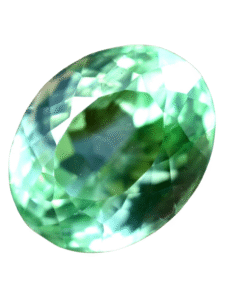
Amblygonite color meanings
Amblygonite is a mineral that can be found in different colors, and each color has been connected with specific meanings in metaphysical traditions. These shades are described in ways that reflect various aspects of thought, emotion, and energy, making the crystal notable for its variety.
- Green: This color is often linked with balance and renewal, as it has been described as supporting emotional stability and natural growth in metaphysical practice.
- Yellow: The yellow form is associated with clarity and optimism, being described as holding energy that reflects brighter perspectives and mental focus.
- Blue: Blue amblygonite is regarded as carrying qualities related to communication and truth, with many connecting it to expressions of honesty and personal understanding.
- White or Colorless: The lighter form is viewed as reflecting purity and openness, where it is often considered part of practices that connect with higher awareness and thoughtful reflection.
- Pink: The pink variation is connected with compassion and emotional warmth, often seen as a color that relates to caring relationships and feelings of kindness.
Where is it found?
Amblygonite is found in several countries across the world, and each location has been noted for producing specimens that vary in appearance and importance to mineral studies.
- Brazil: Significant deposits are found in Minas Gerais and Paraíba, where pegmatite mines have produced material that is well known among collectors and researchers.
- United States: California is recognized for the Pala and Mesa Grande districts that have yielded gem-quality crystals, while the Black Hills in South Dakota are also important mining areas.
- France: The Montebras and Varennes deposits are historically important, since amblygonite was first described there in the nineteenth century.
- Canada: Deposits occur in pegmatite fields, adding to the mineral’s distribution in North America.
- Spain and Germany: Both countries have recorded occurrences of amblygonite within their pegmatite zones, making them notable European localities.
- Namibia: Known for producing specimens with distinct color variations that are valued in mineral collections.
Is it rare?
Amblygonite is not considered one of the rarest minerals, yet it is not commonly found in every location either, which places it in a middle ground between widely available stones and those regarded as extremely scarce. Deposits large enough for commercial extraction exist in countries such as Brazil, the United States and France, but even in those regions the mineral is usually confined to specific pegmatite zones rather than spread across wide areas. Gem-quality material of transparent clarity is much less abundant, and specimens suitable for cutting are harder to obtain compared with more common gemstones. Collectors often value amblygonite for its locality and appearance, and while it is not classified as exceptionally rare, it remains a mineral that is less frequently encountered than many other crystals in the market.
Amblygonite pricing
Prices for amblygonite, much like most crystals/gems, can vary depending on quality, size and whether the specimen is rough, cut or polished, which makes the ranges broad when compared to many other minerals. Smaller rough pieces that are collected for study or display often sell for about $20 to $50, with more distinctive samples moving into higher ranges as their features become more desirable.
When amblygonite is found in polished or tumbled form, the price usually increases, with many stones in this category being listed between $40 and $120 depending on their clarity, finish and overall weight. Cabochons cut for jewelry typically cost more, with prices frequently falling between $100 and $300, especially for stones showing stronger color or greater transparency.
Faceted amblygonite gemstones are more limited, and their scarcity in this form places them in higher categories of pricing compared with rough or tumbled material. Smaller cut stones may be offered around $200 to $400, while larger or well-cut examples can reach ranges of $500 to $1,000 or more in certain markets. Collectors often note that fine faceted pieces remain harder to locate, which explains the higher figures.
Museum-quality crystals or exceptionally large specimens from historic localities can sometimes be valued much higher, depending on demand and the significance of the piece. In these cases, values have been known to exceed $2,000, particularly when the specimen shows clarity, size or provenance that distinguishes it from more typical examples. Overall, amblygonite remains moderately priced in many forms, but premium examples hold ranges that reflect their rarity in the gem trade.
Amblygonite history
Amblygonite’s history in mineralogy begins with its description by August Breithaupt in 1817, when the amblygonite mineral was first identified and distinguished from other phosphate-rich species. The mineral species became notable because of its cleavable structure, showing an obtuse cleavage angle close to 90°, which made it distinct from feldspar and scapolite. Early mineralogists recognized its presence in high-temperature tin veins and greisens, with important deposits reported in Hebron and later studied through collections at institutions such as the Museum of Natural History.
Research on amblygonite crystals expanded in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, when mineral specimens were compared with spodumene and other lithium- and phosphate-rich minerals. The amblygonite-montebrasite series was later defined, with amblygonite being fluorine-dominant and montebrasite being hydroxyl-dominant, while intermediate material showed a mixture of amblygonite and montebrasite. Variants such as natromontebrasite and lacroixite were also examined, broadening the classification of related minerals. Twinning is common within this mineral species, with microscopic polysynthetic twinning often observed during structure refinement studies.
Scientific journals such as American Mineralogist and Canadian Mineralogist published extensive work on its properties, including characterization by single-crystal methods, infrared spectroscopy and multinuclear MAS-NMR. These studies revealed detailed information about crystal pockets, flame test reactions, fluorescence under ultraviolet light and the presence of fluorophosphate components. Amblygonites were documented in equant or tabular forms, sometimes displaying light yellow, pale green or bluish-green coloration. Transparent amblygonite has been cut into faceted gems, although amblygonite rare material of true gem quality remains limited.
Amblygonite gems gained attention because of their scarcity, with amblygonite value dependent on clarity, size and color. Yellow gems and bluish green faceted amblygonite stones represent some of the finest examples of gem material, though the largest cut amblygonite stones remain rare gems mainly preserved in collections. Gem quality amblygonite and faceted amblygonite forms are sometimes used as a gemstone, though the main sources for gem material are Brazil, alongside occurrences in the United States and other regions. Over time, amblygonite forms have become valued both for their rarity and for their contribution to gemology and mineral science, with faceted and used examples holding a permanent place in the history of rare gemstones.
Amblygonite properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | (Li,Na)AlPO4(F,OH) |
| Category | Phosphate mineral |
| Crystal System | Triclinic |
| Color | White, yellow, green, blue, pink, colorless |
| Crystal Habit | Tabular crystals, massive or granular forms |
| Cleavage | Perfect on {100} |
| Fracture | Uneven to subconchoidal |
| Mohs Hardness | 5.5 – 6 |
| Luster | Vitreous to pearly |
| Transparency | Transparent to translucent |
| Specific Gravity | 2.9 – 3.1 |
| Streak | White |
| Refractive Index | 1.578 – 1.646 |

